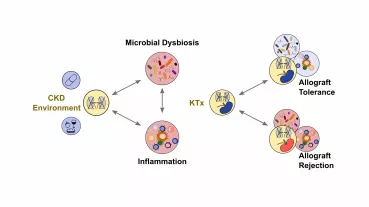
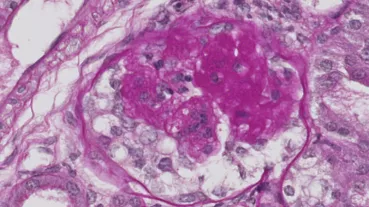
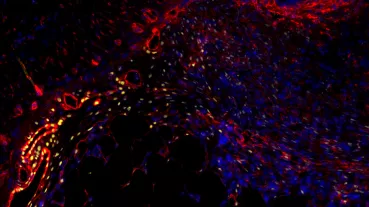
Abdominal Area, Kidneys & Pelvis
|
The role of urethral brush cells in neurogenic in neurogenic inflammation
Funding line:
First and Second Applications
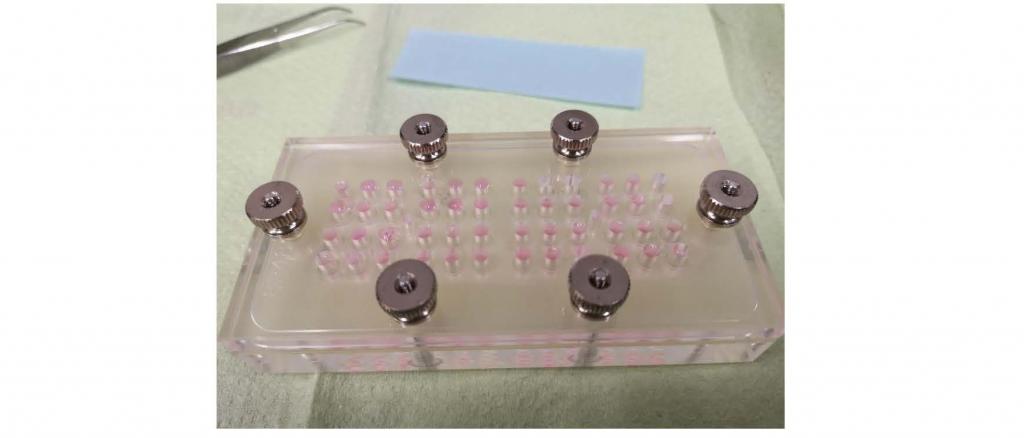
Modified Boyden Chamber for „Cell Migration Assay“
(© Patricia Schmidt)
Urinary tract infections are among the most common bacterial infections worldwide. We found a new cell in the urethra. These urethral brush cells (UBC) use the same mechanisms as taste cells of the tongue to protect the body from infection. They therefore act as sentinals at the entrance of the genitourinary tract. They detect harmful substances (such as bitter substances or bacteria) and induce bladder emptying as a protective measure to flush out the invaders.
Potentially, they may also induce neurogenic inflammation and attract immuncompetent cells.
The aim of this project is to clarify the role of UBC in these mechanisms.