Brain
|
Clinical and experimental evaluation of homoarginine in stroke treatment
Funding line:
Else Kröner Excellence Fellowships
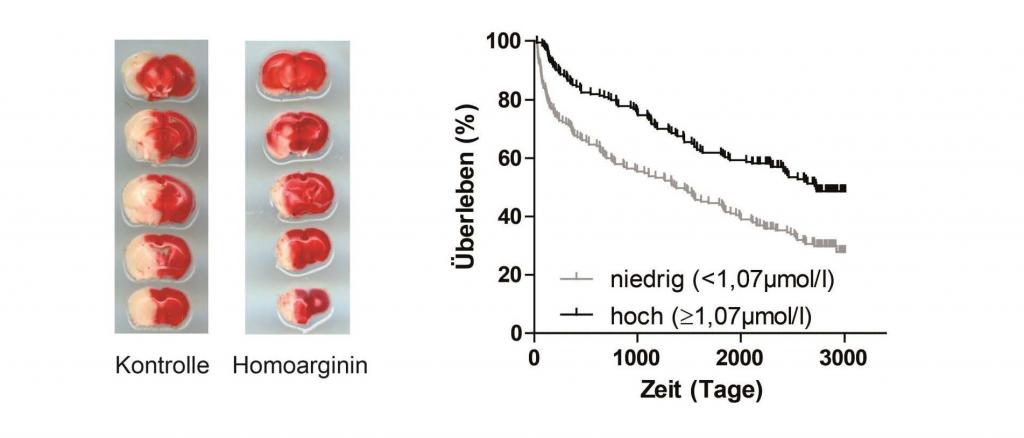
Homoarginine supplementation reduces infact size (white) in experimental stroke models (left) and higher homoarginine levels in patients are associated with increased survival rates after stroke (right)
(© UKE, Chi-un Choe)
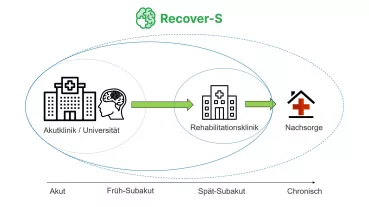
Stroke is the second leading cause of death and major cause of disability worldwide. Recent epidemiological studies revealed that stroke and death rate are higher in people with low blood levels of the amino acid homoarginine. In experimental stroke models, homoarginine supplementation reduced stroke size and disability. Now we aim to normalize low homoarginine levels in stroke patients and we will evaluate clinical and vascular parameters after 6 months. Additional experimental studies will uncover potential underlying mechanisms. We hope that our findings will improve future stroke treatment.
The latest press release can be found here.