Non-invasive monitoring of minimal residual disease and Graft-versus-Host-Disease by circulating nucleic acids after allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation
Although allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT) is an effective curative treatment for several neoplasic and non-neoplasic diseases, the procedure is not devoid of complications. Relapse of the underlying disease and Graft-versus-Host Disease (GvHD) are frequent complications after allo-HCT, they contribute to morbidity and mortality and are the main cause of treatment failure.
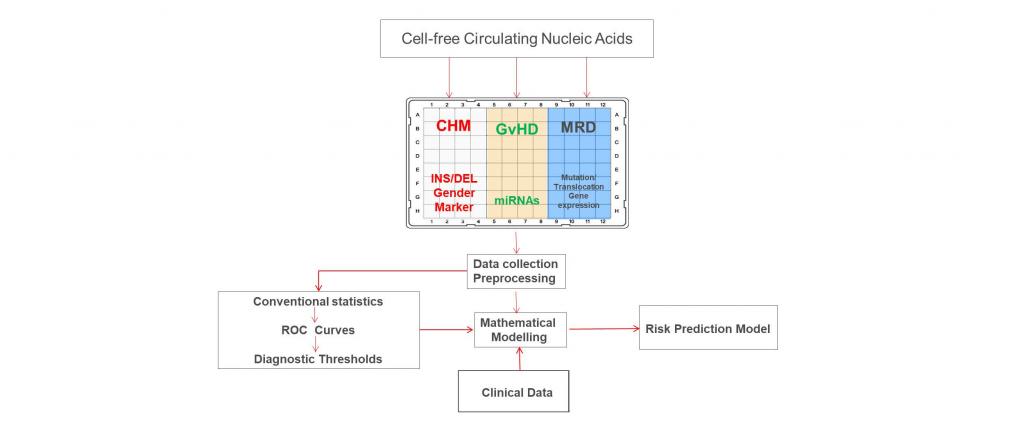
In this project, we aim to establish a non-invasive monitoring, based on circulating nucleic acids, for early detection of relapse and/or GvHD in patients undergoing allo-HCT. We hypothesize that the combination of circulating cell-free nucleic acids analysis together with clinical parameters will result in prediction of relapse and/or GvHD development and will improve diagnostic accuracy.
Here you can get further information.