Human Capacity Building for Quality Eye Health Care in Western Tanzania

Situation:
About four million people in the Rukwa, Katavi and Kigoma regions of Western Tanzania are without adequate eye care. About 0,5 percent of the people are blind and 1,7 percent suffer from moderate or severe visual impairment. Up to 80 percent of visual impairments are avoidable or treatable. Many people‘s life and earning capacity can be improved by improving basic eye care services.
Objectives:
Poor people in the regions of Rukwa, Katavi, and Kigoma have better access to quality eye health services.
- Number of consultations conducted at Dr. Atiman and St. Aloyce eye clinics in Sumbawanga and Mpanda: from 4.500 in 2021 to 20.000 in 2025
- Number of referrals from ophtalmic assistants to the eye clinics: from 200 in 2021 to 400 in 2025
- Number of screenings conducted through hospital outreach: from 350 in 2021 to 1.500 in 2025
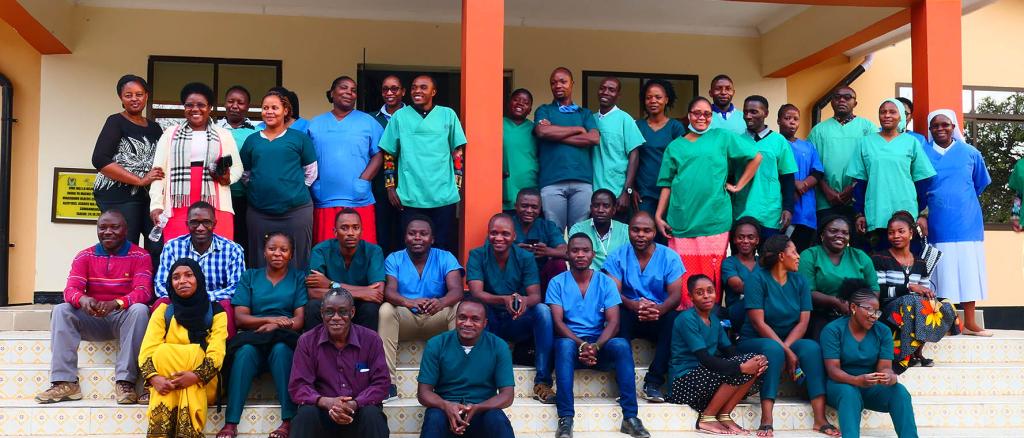
- Train new ophtalmic assistants for Katavi and Kigoma regions
- Improve skills through on-the-job training and supervised practice at eye camps
- Develop, conduct, and evaluate distance trainings for ophtalmic assistants
- Train assistant medical officers and cataract surgeons
- Ensure peer-to-peer learning opportunities and professional supervision at the eye clinics / eye camps
- Develop, conduct, and evaluate distance trainings for eye clinic staff
The professionals trained and educated under the project will be employed and paid by the partner dioceses and/or the government, if not already done. The trained Ophtalmic Assistants are distributed throughout the region and work in premises provided by the diocese or the government. TanZanEye will follow up on the trainings by providing regular opportunities for peer to peer learning and supervision during the eye camps and by providing refresher trainings (once a year) that are supported through e-learning.
- The project creates the personnel prerequisites for being able to offer basic ophthalmic care in rural areas as well.
- The local specialists are further qualified after their initial training through various measures: Learning by doing and supervision during the biannual eye camps, annual trainings, e-learning based on customized content provided on tablets.
Here you can find further information.